循环链表||
题目
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.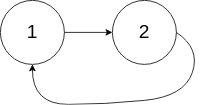
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
解析重点
1.为了知道是否有循环,我们使用通用的方式使用快慢指针。
2.这里重要的是快慢指针相交的点c,他到head点的距离和循环的距离是相等的,那么从head点和交点c出发,他们相等的点就是交点。
java代码
1 | /** |